How Does Metal Detector Work
Hey there, treasure hunters and curious minds! Ever wondered what’s zapping away underground, revealing lost coins, forgotten jewelry, or maybe even a secret pirate stash? Yep, we’re talking about the magical, mystery-solving device known as the metal detector. It’s like a magnet for metal, but way cooler. And guess what? It’s not rocket science! Let’s break down how this nifty gadget works, and by the end of this, you’ll be ready to explain it to your grandma (and she’ll actually understand it, no kidding!).
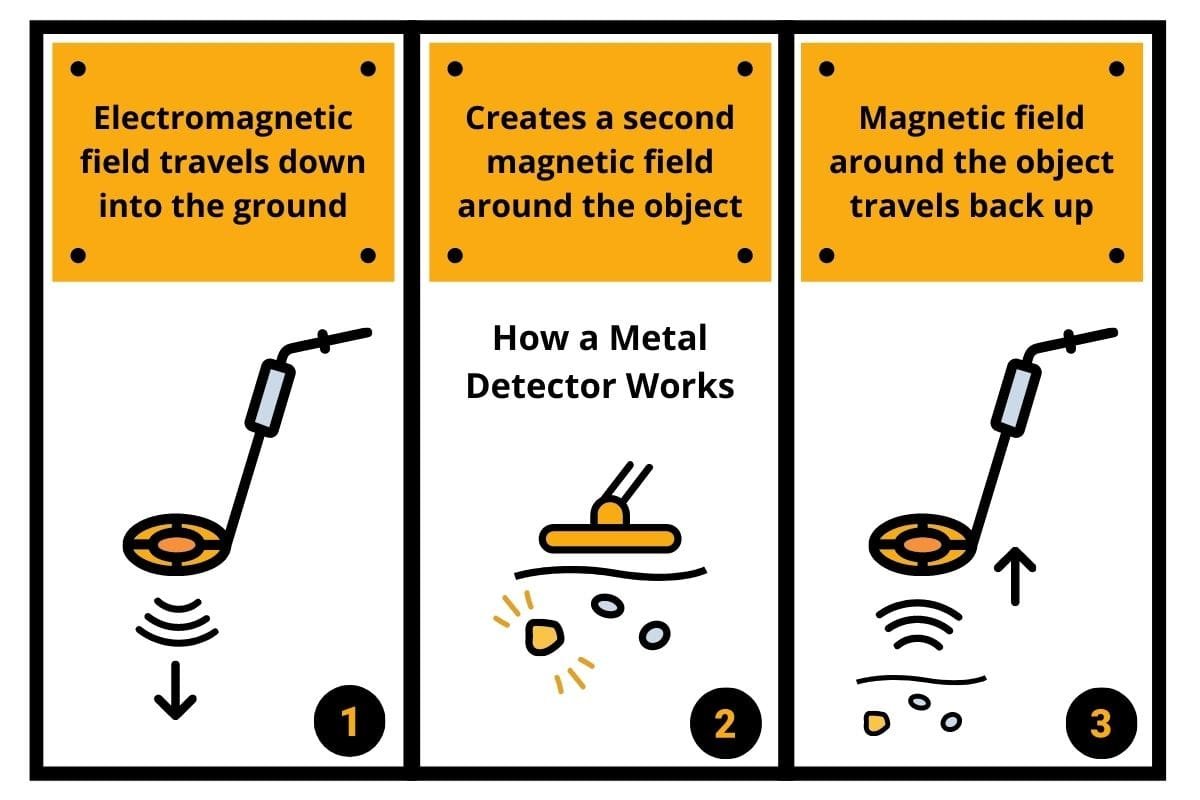
So, imagine you’re walking along, waving this big, frisbee-like thing around. That’s the search coil. Think of it as the detector’s nose. It’s not actually sniffing, of course, but it’s doing some pretty neat electromagnetic sniffing. Inside this coil, there’s wire, and when you turn the detector on, electricity zips through that wire. Now, here’s where the magic starts to brew.
The Electrifying Secret: Electromagnetism, Duh!
When electricity flows through a wire, something awesome happens: it creates an invisible force field around it. This force field is called a magnetic field. Pretty neat, right? It’s like the wire is wearing an invisible superhero cape, but instead of flight, it’s all about magnetism. So, that search coil is essentially a souped-up electromagnet.
Now, this magnetic field doesn’t just hang out. It’s actively pushing outwards, like a friendly wave saying, "Hey, anything metal out there?" This field radiates downwards and outwards from the coil. It’s constantly searching, a tireless explorer of the subterranean realm. Think of it as sending out little magnetic tendrils, exploring every nook and cranny.
But here’s the catch: this magnetic field is usually pretty weak. If it were super strong, it might just pull loose change out of your pocket as you walk! So, it’s a delicate balance of power. The detector is designed to emit a field that’s strong enough to interact with buried metal, but not so strong that it causes chaos.
The Metal-Friendly Encounter
Okay, so we’ve got our invisible magnetic field waving hello to the ground. What happens when it bumps into something made of metal? This is where things get really interesting, and frankly, quite clever.
When the detector's magnetic field encounters a metal object, it doesn't just bounce off like a polite ping-pong ball. Oh no, metal is special! Metal objects are excellent at conducting electricity. Remember that electricity zipping through the coil? Well, metal is like a superhighway for that stuff.
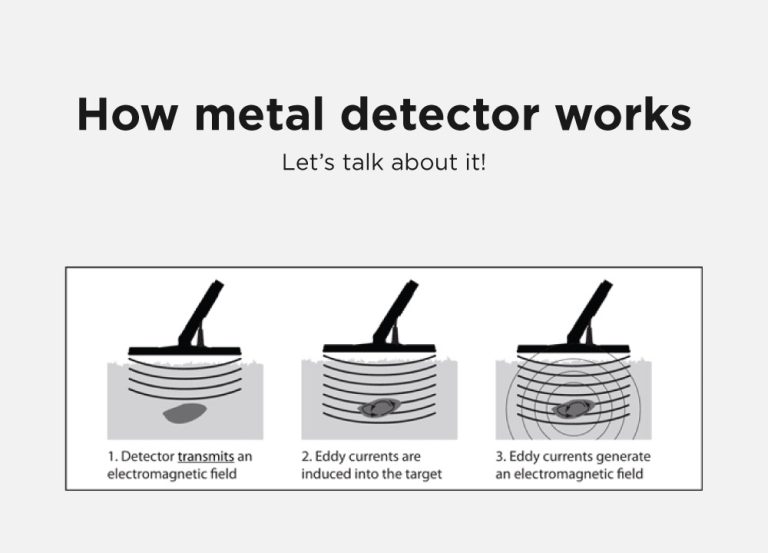
As the detector’s magnetic field hits the buried metal, it makes the electrons in the metal start to move. This is called inducing a current, or more specifically, eddy currents. Imagine the magnetic field tickling the metal, and the metal’s electrons start to dance around, creating their own tiny, little magnetic fields. It's like the metal object gets a little buzzed by the detector's influence and starts to generate its own magnetic hum.
These eddy currents are super important because they generate their own magnetic field, and this new magnetic field is the key to the whole operation. It’s like the buried metal is whispering back to the detector, and the detector is programmed to listen very, very carefully.
The Receiver's Ears: Detecting the Echo
So, we have the initial magnetic field from the coil, and then we have the secondary magnetic field created by the eddy currents in the metal object. Now, how does the detector actually know something is there? This is where the other part of the search coil, or sometimes a separate coil, comes into play. This is the receiver.
Most common metal detectors use a single coil that acts as both a transmitter and a receiver. It's a multitasker, that one! This coil, when not actively transmitting its primary magnetic field, is also incredibly sensitive to other magnetic fields. It’s like it’s constantly listening for whispers in the electromagnetic spectrum.
When those eddy currents in the metal object generate their own magnetic field, this field interacts with the receiver part of the coil. It's like a subtle change in the air, a tiny disturbance in the magnetic force field. The receiver coil detects this disturbance, this tiny magnetic echo from the buried metal.

Think of it this way: you shout into a canyon (the transmitter coil sends out its field). If there's a rock wall far away (the metal object), your shout will bounce back as an echo. The receiver is like your ear, listening for that echo. The strength and timing of the echo tell you how far away the rock wall is and how big it might be.
The Signal Gets Amplified and Translated
This detected signal is usually very, very faint. I mean, we’re talking about whispers in a hurricane here. So, the detector has some serious electronics onboard to take this tiny signal and crank it up. This is the job of the amplifier.
The amplifier takes that faint whisper and turns it into something audible, or at least something the detector's brain can process. It’s like turning a tiny murmur into a clear announcement.
Once amplified, this signal is then processed by the detector's circuitry. This circuitry is the detector's brain. It analyzes the signal to figure out what it might be. Is it a coin? A bottle cap? A rusty nail? The circuitry can often distinguish between different types of metal based on how they affect the magnetic field and the eddy currents they produce. This is where discrimination comes in – the ability to ignore junk and focus on treasure!

Different metals react differently. For example, iron (like a nail) will create a different kind of eddy current and magnetic response than gold or silver. The detector's circuitry is programmed with this knowledge, allowing it to differentiate.
Beep, Boop, Bingo! The Sound of Discovery
And then, the moment we’ve all been waiting for: the audio signal! When the circuitry identifies a signal that matches the characteristics of metal (and hopefully, desirable metal), it tells the speaker to make a noise. Beep! Boop! Ding! Whatever the sound, it’s the detector's way of saying, "Hey! There’s something interesting down there!"
Some detectors have simple beeps, while others have more complex tones that can indicate the type of metal. Higher pitches might mean a smaller, shallower object, while deeper tones could suggest a larger or deeper target. It’s like a secret code between you and the machine.
Many modern detectors also have a visual display. This screen can show you information like the estimated depth of the target, its probable type of metal (often represented by a number on a scale), and even the shape of the object. It’s like having a treasure map right in front of you, albeit a slightly abstract one!
Two Main Flavors of Detectors: VLF and PI
While the core principle is the same, there are a couple of main types of metal detectors you'll encounter:

VLF (Very Low Frequency) Detectors: These are the most common type, especially for hobbyists. They typically use two coils: one for transmitting the magnetic field and another for receiving the signal. This allows them to be quite good at discriminating between different types of metal, meaning they can ignore iron junk and help you find that sparkly treasure. They’re like the polite detectives who ask for identification before letting you pass.
PI (Pulse Induction) Detectors: These detectors often use a single coil that rapidly pulses its magnetic field. When the pulse ends, the coil listens for any lingering magnetic signals from the ground. PI detectors are generally less affected by mineralized soil (which can fool VLF detectors) and can often detect deeper. However, they tend to be less effective at discriminating between different types of metal. They're more like the enthusiastic, but sometimes a bit oblivious, search party. "IS IT METAL? YES? LET'S DIG!"
Beyond the Beep: Factors Affecting Detection
It’s not just about waving the detector around. A few things can make your treasure hunting more or less successful:
- Depth of the Object: The deeper the metal, the weaker the signal will be when it reaches the detector.
- Size of the Object: Larger objects generally produce stronger signals. A tiny earring might be harder to find than a large pot.
- Type of Metal: As we mentioned, different metals react differently.
- Ground Mineralization: Some soils have a lot of iron or other minerals that can create their own weak magnetic fields, potentially interfering with the detector.
- Coil Size and Type: Different coils are designed for different purposes. Smaller coils are better for pinpointing and finding small targets, while larger coils can cover more ground and detect deeper.
So, the next time you see someone with a metal detector, you can nod knowingly and think, "Ah, they’re just harnessing the power of electromagnetism to uncover hidden wonders!" It’s a fascinating dance between electricity, magnetism, and the earth beneath our feet.
And there you have it! Metal detectors aren't really powered by magic, but by some seriously cool science. They're ingenious tools that turn invisible forces into tangible discoveries. So go forth, my friend, and may your beeps lead you to gleaming treasures and delightful surprises. Happy hunting – the ground is full of stories waiting to be unearthed!