Is A Covalent Bond Between Two Nonmetals

Hey there, fellow curious minds! Ever find yourself wondering about the tiny, invisible dance happening all around us? You know, the stuff that makes up everything? Today, we're going to chat about something super fundamental, a little secret that chemists are quite fond of: the covalent bond between two nonmetals. Don't let the fancy name scare you off! Think of it less like a complex equation and more like a cozy partnership, a shared commitment that makes the world go 'round.
Imagine you've got two friends who both really love a particular video game. They don't want to just play separately; they want to team up, share their controllers, and conquer virtual worlds together. That's kind of what's happening at the atomic level when two nonmetal atoms decide to form a covalent bond. They're not really giving anything away permanently; instead, they're deciding to share their electrons. It's like a potluck dinner for atoms – everyone brings something to the table, and everyone gets to enjoy the delicious outcome!
So, what exactly are these "nonmetals" we're talking about? Think of elements like oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and chlorine. These are the building blocks of so many things we encounter every single day. They're not the shiny, metallic types that conduct electricity and get all warm and fuzzy when you rub them. Nonmetals are a bit more... reserved, shall we say. They're the quiet achievers, the backbone of our existence.
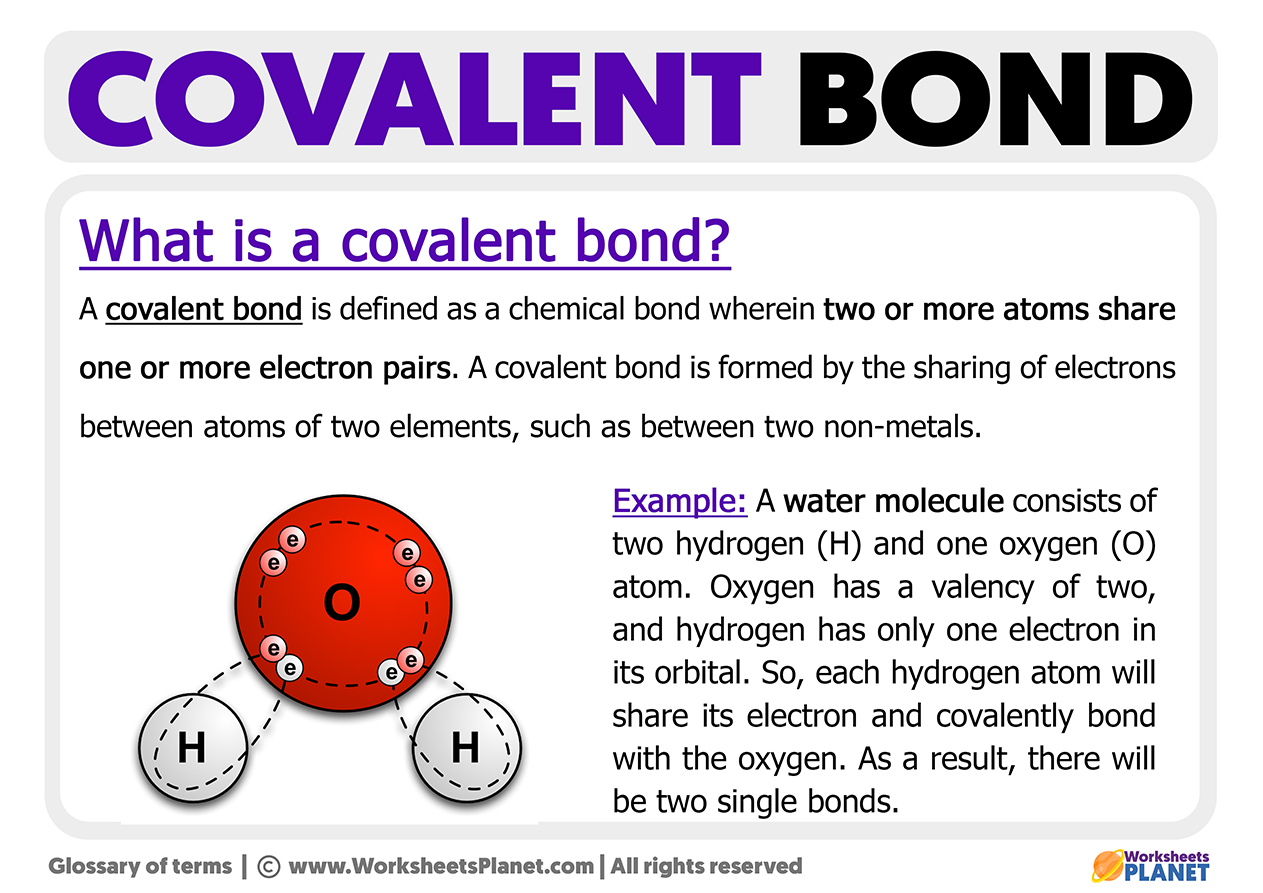
Let's take water (H₂O) as a prime example. It's what we drink, what we swim in, what our plants crave. It's literally life! And guess what? Water is formed from covalent bonds between oxygen and hydrogen atoms. The oxygen atom needs a couple of electrons to feel complete, and each hydrogen atom needs one. So, they decide to share! The oxygen atom offers up one of its electrons, and each hydrogen atom offers up its single electron. Now, they're all happily sharing, creating a stable little molecule that allows us to live our best lives. Pretty neat, huh?
Think of it like a couple sharing a blanket on a chilly evening. Neither person wants to give up the entire blanket, but by both snuggling close and sharing its warmth, they both feel comfortable and secure. That's the essence of a covalent bond. The atoms are holding onto their electrons, but they're also allowing their neighbors to get a taste of that electron goodness. This sharing creates a powerful attraction, a sort of atomic hug that keeps them together.

Why should you even care about this atomic huddle? Well, my friends, it's because these covalent bonds are the reason we have air to breathe, food to eat, and even the very screens you're reading this on! Take the air around you. It's mostly made of nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂). Yep, both of those are pairs of nonmetal atoms happily sharing their electrons. Without these covalent bonds, the nitrogen and oxygen atoms would be floating around all by themselves, perhaps not quite as stable or ready to form the complex molecules that make up our atmosphere.
Let's get a little more personal. Think about the plastic in your water bottle, the cotton in your favorite t-shirt, or the wood in your furniture. All of these are built on a foundation of covalent bonds, primarily involving carbon atoms linked with other nonmetals like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Carbon is like the master architect of the molecular world, and its ability to form strong covalent bonds with itself and other nonmetals is what allows for the incredible diversity of organic compounds. It's like having Lego bricks that can connect in endless ways to build amazing structures!

It’s also about understanding why things behave the way they do. Why does salt (sodium chloride) dissolve in water, but oil doesn't? Well, salt is an ionic compound (where electrons are transferred, not shared), and water is a polar covalent molecule (meaning the sharing isn't perfectly equal, creating a slight positive and negative end). Oil, on the other hand, is made of nonpolar covalent molecules. It's like trying to mix oil and water – they just don't want to hang out together. Understanding covalent bonds helps us make sense of these everyday observations.
Consider the process of cooking. When you bake a cake, chemical reactions are happening. New covalent bonds are forming, and old ones are breaking, transforming simple ingredients into deliciousness. The proteins in an egg, the carbohydrates in flour – they are all intricate networks of atoms held together by covalent bonds. Even the sizzle you hear when you fry an egg is a testament to the energy released or absorbed when these bonds are rearranged.
It's not just about the big, tangible things. Think about the energy that powers your life. Photosynthesis, the process plants use to convert sunlight into energy, involves the formation of covalent bonds in sugars. Cellular respiration, the way our bodies extract energy from food, breaks down covalent bonds. These bonds are like tiny batteries, storing and releasing the energy that fuels life itself.
So, the next time you take a sip of water, breathe in the air, or marvel at a beautiful piece of wood, take a moment to appreciate the incredible teamwork happening at the atomic level. That seemingly simple covalent bond between two nonmetals is a fundamental force, a quiet yet powerful partnership that makes our world possible. It’s a reminder that even the smallest interactions can lead to the most magnificent outcomes. It’s the universe's way of saying, "Hey, let's all chip in and make something amazing together!" Isn't that a rather lovely thought?