Nonmetallic Elements That Are Held Together By Covalent Bonds

Ever wondered what makes the world go 'round? Well, it’s not just gravity and good vibes (though those help!). Deep down, at the atomic level, it’s the incredible way atoms link up to form everything we see and touch. Today, we’re diving into a particularly fascinating group of these atomic buddies: nonmetallic elements held together by covalent bonds. Think of it as the ultimate cosmic handshake, where atoms share their electron toys instead of one hogging them all. And guess what? This sharing is the secret sauce behind so many things we use and love every single day!
Why is this topic so much fun? Because it’s the foundation of life itself! From the air we breathe to the water we drink, from the food we eat to the devices we use to read this, covalent bonds between nonmetals are the unsung heroes. They’re not just about dry chemistry; they’re about the building blocks of our reality. Understanding this concept is like unlocking a secret level in the game of life, revealing the elegant simplicity and ingenious design that underpins our universe.
The Power of Sharing: What Are Covalent Bonds?
So, what’s the deal with these covalent bonds? Imagine atoms as little kids who each have a certain number of toy cars (electrons). Some kids are happy to just hold onto their cars, while others might want to borrow or trade. In a covalent bond, two or more nonmetallic elements decide to pool their resources. They share their electrons, forming a super-strong connection that holds them together. It's a cooperative effort, a mutual agreement for the good of the whole molecule. This sharing is key because it allows these atoms to achieve a more stable, happy state, much like us when we feel secure and connected.
The benefit of this atomic sharing is immense. Covalent bonds create molecules that are stable and versatile. They are the backbone of organic chemistry, which, as you might guess from the name, is the chemistry of life. Think about it: every living organism on Earth is a masterpiece of covalent bonding. Carbon, in particular, is the superstar of covalent bonding, able to form long chains and complex structures that are the foundation of DNA, proteins, and all the organic molecules that make us, well, us!
Everyday Heroes: Common Nonmetals and Their Covalent Creations
Let’s meet some of the main players in this covalent bonding drama. You’ve definitely heard of them:
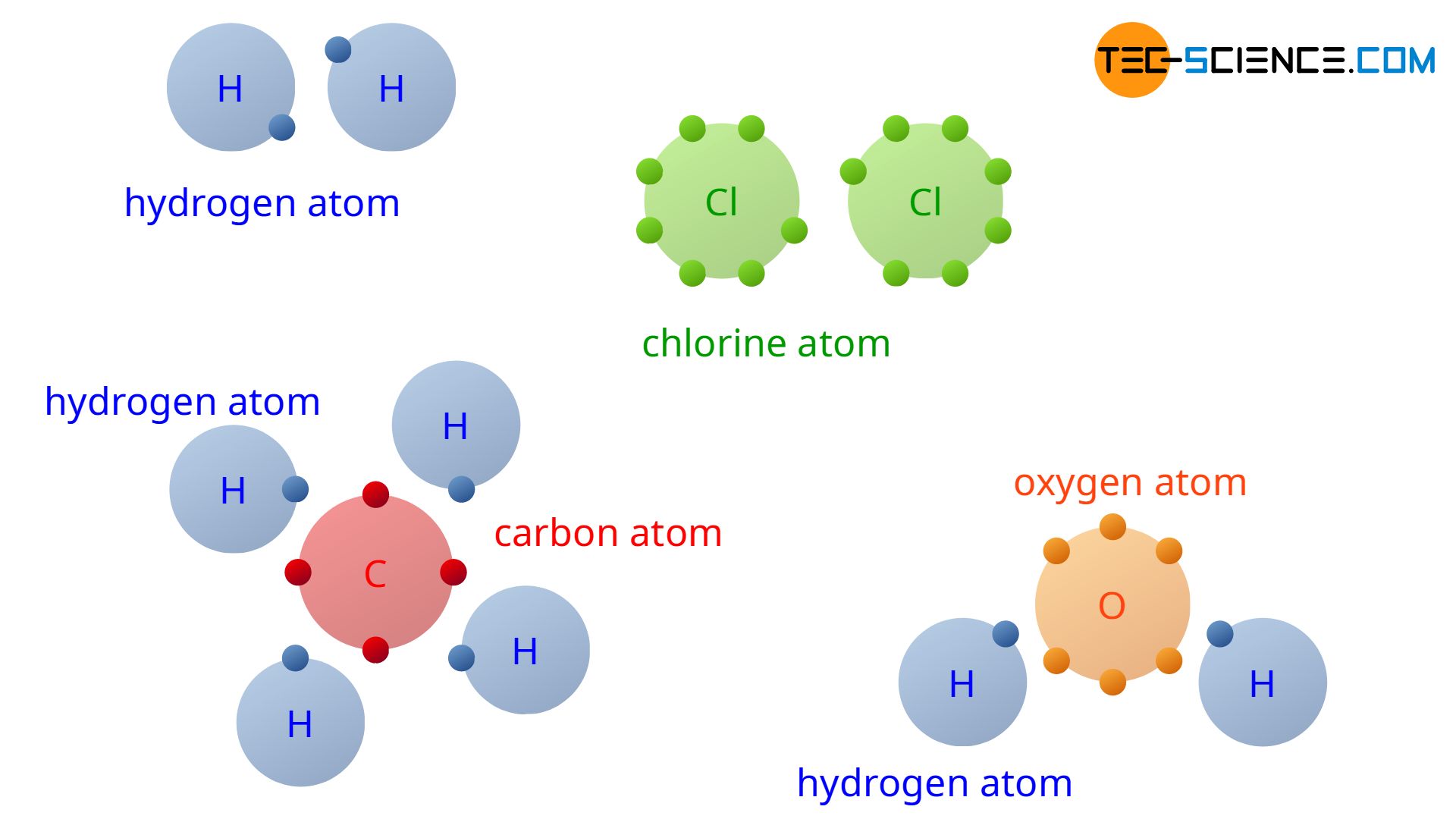
- Oxygen (O): The life-giver! In its most common form, O2, two oxygen atoms are covalently bonded. This is what we breathe to survive. And then there’s water (H2O), where oxygen forms covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms. Without these bonds, the very act of breathing and hydration would be impossible.
- Hydrogen (H): The most abundant element in the universe, hydrogen is a frequent partner in covalent bonding. It's the 'H' in water and a crucial component of countless organic molecules.
- Nitrogen (N): Making up about 78% of the air we breathe, nitrogen also forms diatomic molecules (N2) with a strong covalent bond. It’s also essential for building proteins and DNA.
- Carbon (C): As mentioned, carbon is the king of covalent bonding. It can bond with itself and with many other nonmetals to create an astonishing variety of molecules. Think of the complex structures in plastics, fuels, and all living tissues – all thanks to carbon’s incredible bonding ability.
- Sulfur (S): Found in proteins and in important molecules like sulfuric acid, sulfur also participates in covalent bonds, contributing to the structural integrity and functionality of many substances.
- Phosphorus (P): Essential for life, phosphorus is a key component of DNA and ATP (the energy currency of our cells), forming covalent bonds within these vital structures.
These elements, when linked by covalent bonds, form an incredible array of compounds. Consider methane (CH4), the simplest organic molecule, which uses carbon to covalently bond with four hydrogen atoms. It’s a key component of natural gas. Or think about ammonia (NH3), where nitrogen covalently bonds with three hydrogen atoms, a vital compound in fertilizers and cleaning products.
Why This Matters to You
So, why should you care about atoms sharing electrons? Because it directly impacts your life in countless ways:

- Health and Biology: All the essential molecules in your body – from the DNA that makes you unique to the proteins that build your muscles and enzymes that digest your food – are held together by covalent bonds between nonmetals.
- Materials Science: From the durable plastics in your phone and car to the fibers in your clothes, covalent bonds are responsible for creating materials with specific properties. The strength and flexibility of many materials are a direct result of the way atoms are covalently linked.
- Energy: The fuels that power our world, like natural gas (methane) and gasoline, are hydrocarbons – molecules made of carbon and hydrogen linked by covalent bonds. Burning these fuels releases energy, a testament to the strength of these bonds.
- Environment: The air we breathe (O2, N2), the water we drink (H2O), and even pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) are all formed through covalent bonding. Understanding these molecules helps us understand and address environmental issues.
It's truly amazing how the simple act of nonmetallic elements sharing their electrons creates the complex, vibrant, and functional world we inhabit. The next time you take a deep breath, sip some water, or marvel at a piece of technology, remember the silent, powerful forces of covalent bonds at work, tirelessly building and sustaining our reality. It’s a beautiful symphony of sharing, and we’re all beneficiaries of this fundamental atomic dance.
"The structure of matter is based on the rules of chemistry, and the rules of chemistry are based on the rules of physics. And the rules of physics are based on the rules of mathematics. So, in the end, everything is based on mathematics." – Richard Feynman. While Feynman spoke broadly, the elegance of covalent bonding is a perfect example of this principle in action!