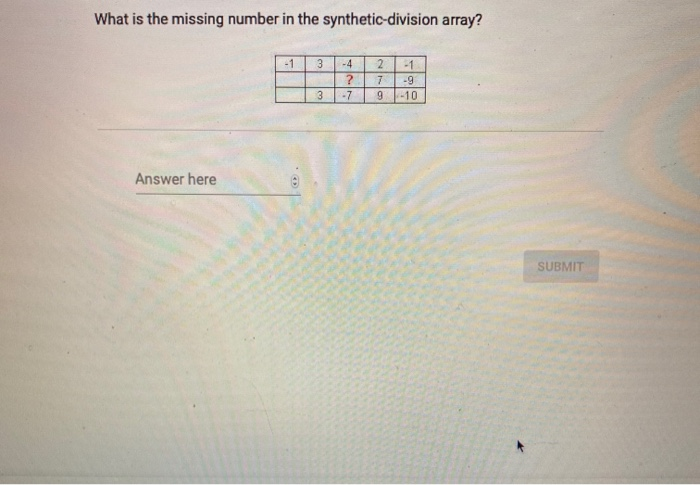
What Is The Missing Number In The Synthetic-division Array
Ever found yourself staring at a string of numbers, seemingly organized but with a curious blank space, and wondered, "What's the missing piece?" Well, that's exactly the kind of intriguing puzzle we're going to unravel today! We're diving into the world of synthetic division, specifically focusing on the often-overlooked but incredibly useful "missing number" in its array. It might sound a bit technical, but trust me, understanding this little quirk can be surprisingly fun and quite illuminating, especially when it comes to tackling polynomial equations. Think of it as a secret handshake that unlocks a quicker way to solve some pretty complex math problems.
So, what exactly is this missing number and why should we care? At its heart, synthetic division is a shortcut method for dividing a polynomial by a linear factor (something like x - c). It’s like a streamlined algorithm that replaces long division, saving you time and reducing the chances of making calculation errors. The "missing number" we're talking about comes into play when the polynomial we're dividing doesn't have a term for every power of x, starting from the highest down to the constant. For instance, if you have x³ + 2x - 5, you're missing an x² term. The synthetic division array requires a placeholder for this missing term, and that placeholder is usually a zero. This zero acts as a silent guardian, ensuring the entire division process flows correctly, maintaining the integrity of the coefficients for each power of x.
The benefits of mastering this are pretty significant. Not only does it make polynomial division more manageable, but it's also a crucial stepping stone for understanding the Factor Theorem and the Remainder Theorem. These theorems allow us to quickly determine if a number is a root of a polynomial (meaning the polynomial equals zero at that number) and what the remainder is when dividing. This is invaluable in algebra, particularly when you're trying to find the roots of higher-degree polynomials, which often appear in fields like engineering, physics, and economics. In an educational setting, it's a core technique taught in pre-calculus and algebra II, making it a foundational skill for anyone pursuing STEM fields.
While you might not be plugging numbers into a synthetic division array to calculate your grocery bill (though you could if you were feeling particularly ambitious!), the principles of looking for patterns and missing information are everywhere. Think about decoding a simple cipher where a letter is missing, or even in everyday problem-solving where identifying an unstated assumption is key. To explore this yourself, start with simple polynomial division problems. Look at the polynomial's terms and note any missing powers of x. When you set up your synthetic division array, remember to insert a zero for each missing power. Websites like Khan Academy offer excellent interactive tutorials and practice problems to get you started. Don't be afraid to play around with it; the more you practice, the more intuitive the "missing number" and the entire synthetic division process will become. It’s a little bit of mathematical detective work that pays off handsomely!